Knowing All Your G’s – What is 2G, 3G, 4G and So On
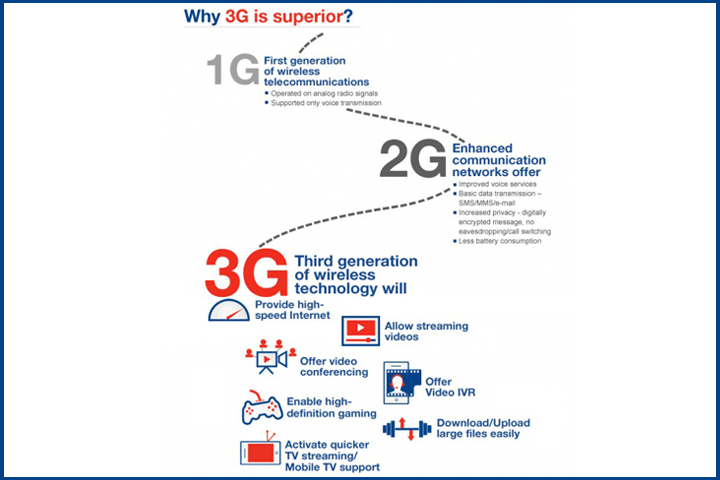
Table of Contents
Not many years ago, mobile phones were just a medium to talk, albeit with increase mobility, but well you could not do much more than talk. The bulky pieces did not even fit in our pockets, but still many of us flaunted them with much gusto to the entire world, whoever was lucky enough to have one of them. The calls cost us a bomb, but well, who cared about the cost when you can talk on your new shiny mobile phones while strutting on the streets in your best suit.
 Then came the great revolution in the technology, and suddenly your humble phone turned into cell phone, smartphone, superphones and what not! Phones are now not just meant for calls but for Facebooking, Instagramming, Messaging, Whatsapping and so much more. We have happily left our old bulky phones behind and landed on the supersonic fast 4G ones. But with so many generational changes in wireless networks, things are starting to look a little bit confusing. In the past ten years, we have seen an exponential evolution of wireless services that we use every day. So let’s take a walk down the history lane and understand the nuances of each generation.
Then came the great revolution in the technology, and suddenly your humble phone turned into cell phone, smartphone, superphones and what not! Phones are now not just meant for calls but for Facebooking, Instagramming, Messaging, Whatsapping and so much more. We have happily left our old bulky phones behind and landed on the supersonic fast 4G ones. But with so many generational changes in wireless networks, things are starting to look a little bit confusing. In the past ten years, we have seen an exponential evolution of wireless services that we use every day. So let’s take a walk down the history lane and understand the nuances of each generation.
1G – When life was much simple
Back in the old days nobody wanted any data plan or pricey video calls, and 1G was the first step to fulfill our dream. Though there were lot many wireless networks before 1G, however the group of TACS, AMPS and NMT is commonly considered to the first and was marked as the first generation of wireless network namely 1G. 1G was the first network ever that made mobile phones consumer-friendly and practical for the masses. It was simply designed for making voice calls and nothing else. And that was also considered a big achievement in those days. Modems did exist on some cell phones, but the analog cellular connections made far more noise than conventional landlines to be fully functional, and anyways the transfer speeds ran on a snail’s pace, to make it work.
2G- The onset of something new
The early nineties saw the rise of 2G services that ushered the mobile phones in a new era. Sound quality improved, security got strengthened and the total capacity was increased. Many networks also started supporting text messages that upped the game. The data also transferred faster, at a speed of 14.4kbps that matched the speed of mid-nineties landline modem model.2G also utilized various other digital protocols including PDC, CDMA, and TDMA among many. GSM supported circuit-switched data (CSD), allowed users to digitally dial-up calls and connect to the internet, though at very high cost.
2.5 G – Oh yes, we did not landed directly to 3G
2.5 G begin the GPRS technology- the most treasured moment in cellphone technology. It provided data services that were “always-on” where ever and whenever we need it. It marked a huge change from the CSD services where we had to dial-up to get connected to the internet. The GPRS worked superfast to get you seamlessly connected to the internet. It was way too fast than any other existing network, including CSD. For the first time, the operators started marking up the fees not by the minute but rather by the usage of the data downloaded.
GPRS was the turnaround that digital wireless technology needed. It gave freedom to the new aspiring herd of young techies to explore the opportunities of the internet on the go. Needless to say, it was a huge hit, and as it was further supported by increasing technologically efficient smartphones, it found many takers for the same. However, even though, the technology had much to offer it was still away from being called 3G as ITU had already drawn the line as to what encompasses a technology to be called 3G. It required speed of 2MPBS and mobile speeds of 385kbps that GPRS was not ready to undertake.
3G- The game changer
3G networks were not the direct upgrades of 2G networks and operated on entire different frequencies and spectrums, leading the need to build entire new networks to support their frequencies. This also led to some of the biggest scams in the world to sell new spectrums to players.
The most significant features of 3G are the huge capacity and broadband capabilities to support a massive number of data and voice customers at a much lower cost. A 3G connection grants you internet speed of more than 400/kbps. 3G made possible real-time conferencing, quicker download of videos images, music and much more. You can access emails, play powerful games, and perform major financial transactions at the tip of your fingers. Forget old pace data services, 3G changed the way we look at smartphones. It even pushed smartphones to develop better hardware to support the mammoth speed of 3G.
4G- Yes, there is still more to come
4G is ten times faster than 3G, delivering a speed of 10megabites per second. Though 4G is still not available in all the countries by all the service providers, it is considered as the next in-thing that will
If you are forever downloading YouTube videos, watching movies while on the go, or you need a slew of apps to get through your day, then 4G will make your life much easier. However, still not all carriers provide 4G and smartphones are still gearing up to adapt to 4G.
And where it is going to end?
The data downloads are getting huge every year, and downloads of this year might exceed 1,000,000,000GB, and that’s a whole lot of data. It is no surprise that smartphones are fueling this growth with their ever-expanding hardware capabilities. As 5G is also coming to the smartphones in the near future, we are on track to a much glorious future.